Learn how to provision and interact with a backend data from code in a jiffy using Prisma + graphql!
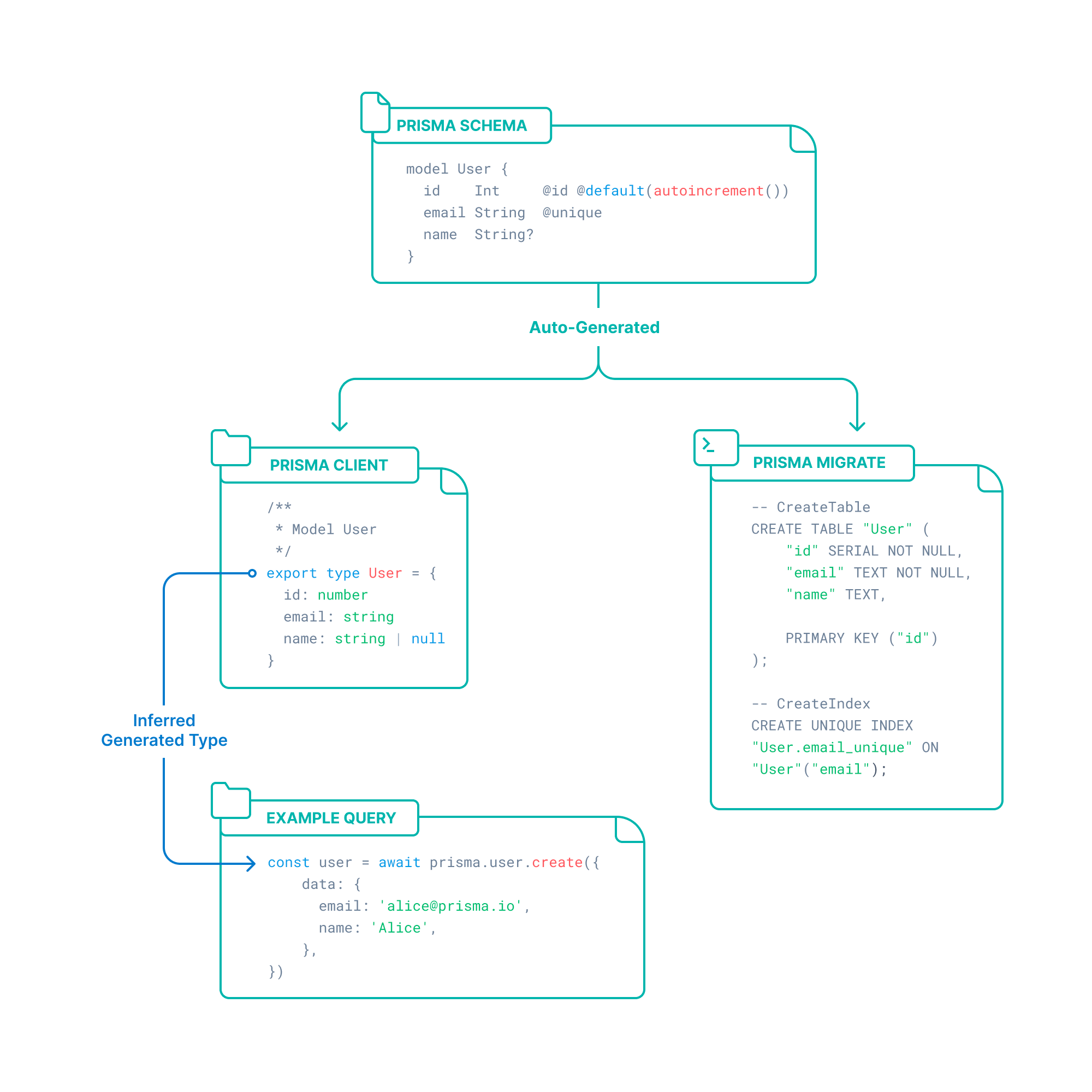
Prisma is an open-source ORM for Node.js and TypeScript. It is used as an alternative to writing plain SQL, or using another database access tool such as SQL query builders (like knex.js) or ORMs (like TypeORM and Sequelize). Prisma currently supports PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQL Server, SQLite, MongoDB and CockroachDB (Preview).
What is a database?
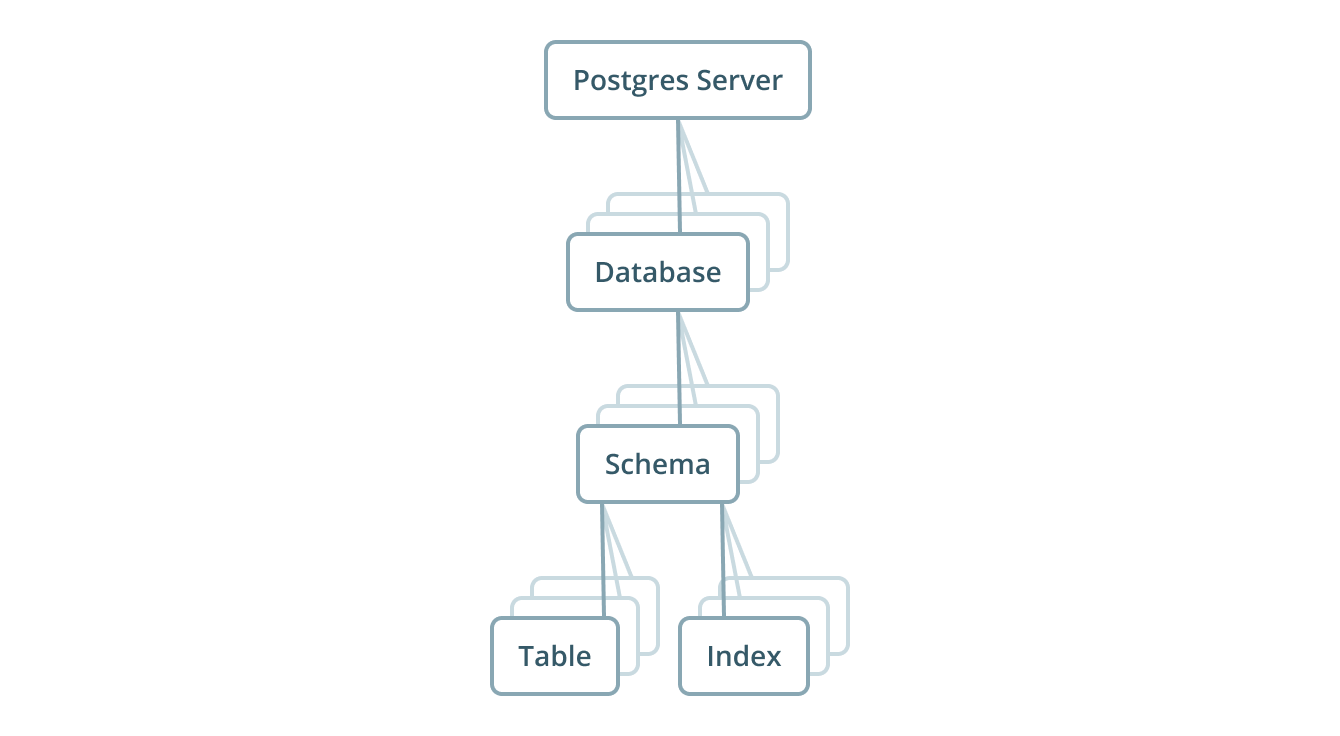
A database is a tool used by developers to store and manage data for their applications. Think of it as a large electronic filing cabinet where you can store information and retrieve it quickly and easily. Databases are an essential component of many modern applications, from simple websites to complex enterprise systems.
There are many different types of databases, but they all share some common features. At its core, a database consists of one or more tables that store information in a structured way. Each table contains rows and columns, with each row representing a single record and each column representing a specific piece of information about that record.
Databases are used to store and manage all types of data, such as customer information, financial transactions, and inventory records. They are also used to track user activity, store log files, and manage security credentials.
In addition to storing data, databases can also perform a wide range of operations on that data, such as searching, sorting, filtering, and aggregating. This makes it easy for developers to extract the information they need from the database and use it in their applications.
Overall, databases are an essential tool for developers who need to store and manage large amounts of data in a structured and efficient way. They help developers build more powerful, flexible, and scalable applications that can handle a wide range of use cases and data types. If you are new to development, it's important to understand how databases work and how to use them effectively to build robust and reliable applications.
Anatomy of the database
Setup the backend side
#
# ____ ____ __ __
# / __/_ __/ / /____/ /_____ ______/ /__
# / /_/ / / / / / ___/ __/ __ `/ ___/ //_/
# / __/ /_/ / / (__ ) /_/ /_/ / /__/ ,< ____
# /_/ \__,_/_/_/____/\__/\__, _/\___/_/|_/ / /__ ____ ____
# / ___/ __ \/ / / _ \/ __ `/ _ \
# we learn & earn 🚀 / /__/ /_/ / / / __/ /_/ / __/
# https://fullstack.college \___/\____/_/_/\___/\__, /\___/
# /____/
#
version: "3"
services:
fullstack.college-postgresql:
container_name: fullstack.college-postgresql
image: postgres:latest
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: fullstack.college
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: fullstack.college
networks:
- fullstack.college
ports:
- "5432:5432"
volumes:
- fullstack.college-postgresql:/var/lib/postgresql/data
fullstack.college-pgadmin:
image: dpage/pgadmin4
container_name: fullstack-pgadmin
depends_on:
- fullstack.college-postgresql
ports:
- "5050:80"
networks:
- fullstack.college
environment:
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL: fullstack@fullstack.college
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD: fullstack
volumes:
- fullstack.college-pgadmin:/var/lib/pgadmin
volumes:
fullstack.college-postgresql:
fullstack.college-pgadmin:
networks:
fullstack.college:
Start the services
docker-compose up -dTo view the output and logs of the services run:
docker-compose logs -fTo stop viewing the logs press CTRL + C on windows or CMD + C on mac.
Variables
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Admin web UI | http://localhost:5050 |
| Connection string | postgres://fullstack.college:fullstack.college@localhost:5432 |
| Hostname | localhost |
| Port | 5432 |
| Username | fullstack.college |
| Password | fullstack.college |
See also
Setup the application side
Installation
npm install prisma --save-dev
npm install @prisma/clientInitialization
Initialize a prisma.schema file:
npx prisma initConfiguration
Tell prisma what database to use and connect to:
datasource db {
provider = "postgres"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client-js"
}Define your first tables
model User {
id Int @default(autoincrement()) @id
email String @unique
name String?
posts Post[]
}
model Post {
id Int @default(autoincrement()) @id
title String
content String?
published Boolean? @default(false)
author User? @relation(fields: [authorId], references: [id])
authorId Int?
}Update the database
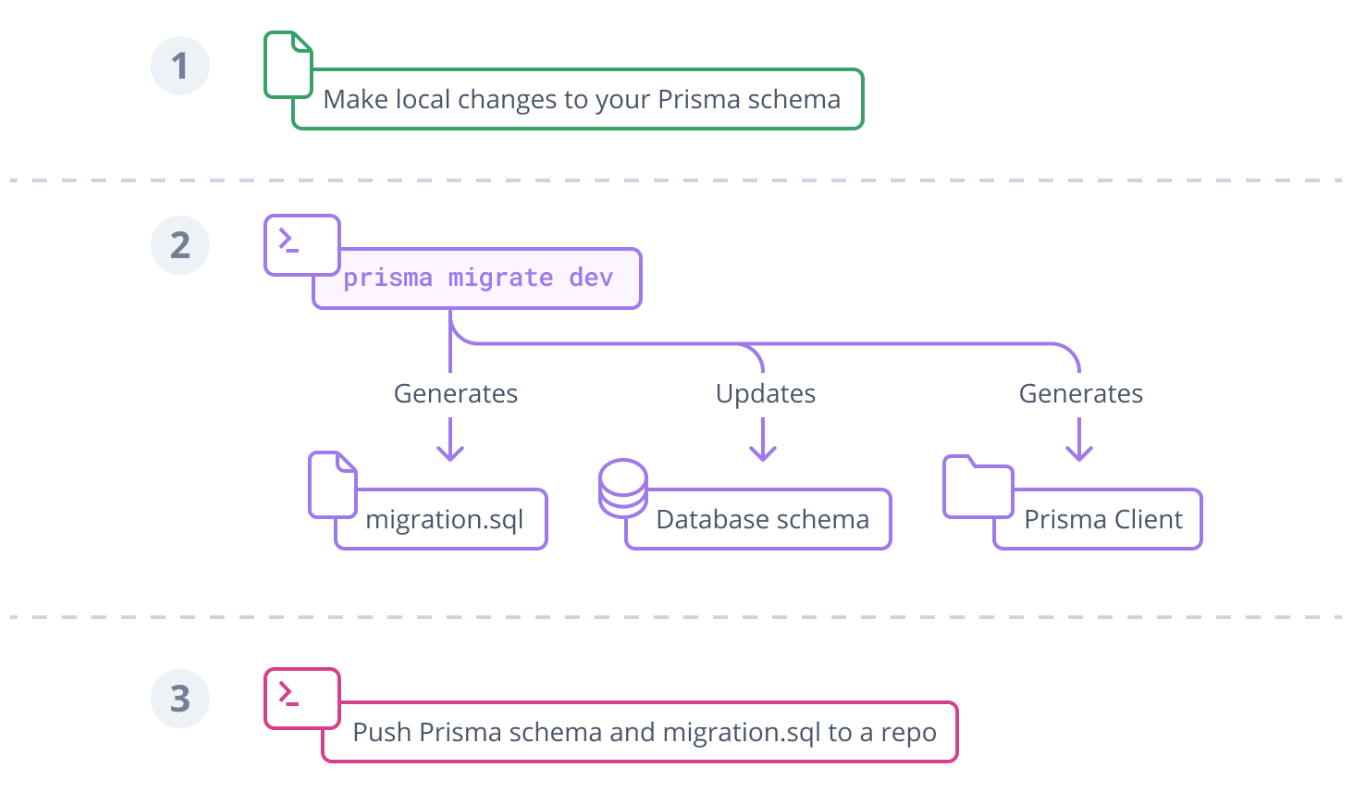
prisma migrate dev --name initPutting it all together